Predicted Molecular Weight: 95 kDa
SDS PAGE Molecular Weight: The migration range of the dimer protein with glycosylation under non-reducing condition is ~190 kDa on SDS PAGE.
Protein Construct: FGFR2 dimer protein contains a FGFR2 extracellular domainfused with a proprietary dimer motif followed by a His tag at the C-terminus.
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) is a cell surface receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily and a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase that belongs to the FGFR family. FGFR2 is also known as BBDS, BEK, brefeldin A resistance factor 1 (BFR-1), cluster of differentiation 332 (CD332), CEK3, CFD1, ECT1, JWS, K-SAM, keratinocyte growth factor receptor (KGFR), TK14, and TK25. FGFR2, a Type I transmembrane protein, contains an extracellular domain with three immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) subdomains (D1, D2 and D3), followed by a transmembrane, and an intracellular domain. Dimerization of FGFRs is necessary for activation and they can homodimerize and heterodimerize in both the presence and absence of ligand. FGFRs bind fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) leading to phosphorylation and triggering signaling cascades. Mutations in FGFR2 cause pathological ligand-independent dimerization, leading to uncontrolled signaling in both developmental disorders and cancers. Mutations in the FGFR2 gene are the cause of several craniosynostosis syndromes and FGFR2 is involved in various forms of cancer including gastric cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer. While structurally and functionally similar to human FGFR2 homodimer, Rhesus macaque FGFR2 homodimer is a species-specific tool essential for preclinical studies, basic research, and translational research.
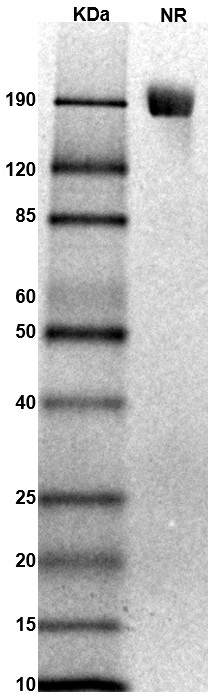 MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: FGFR2 dimer under non-reduced condition
MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: FGFR2 dimer under non-reduced condition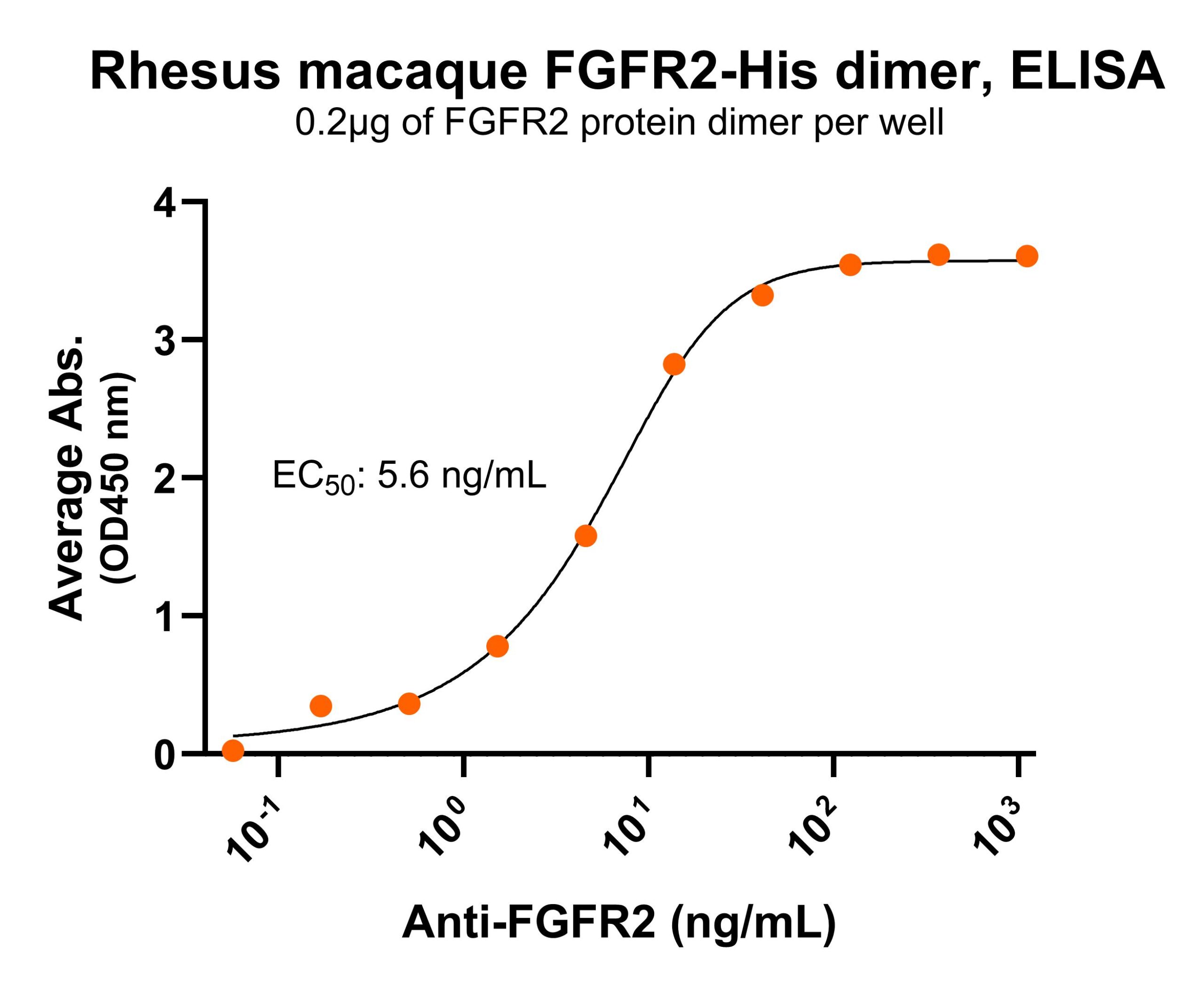 Immobilized Rhesus macaque FGFR2 protein dimer
Immobilized Rhesus macaque FGFR2 protein dimer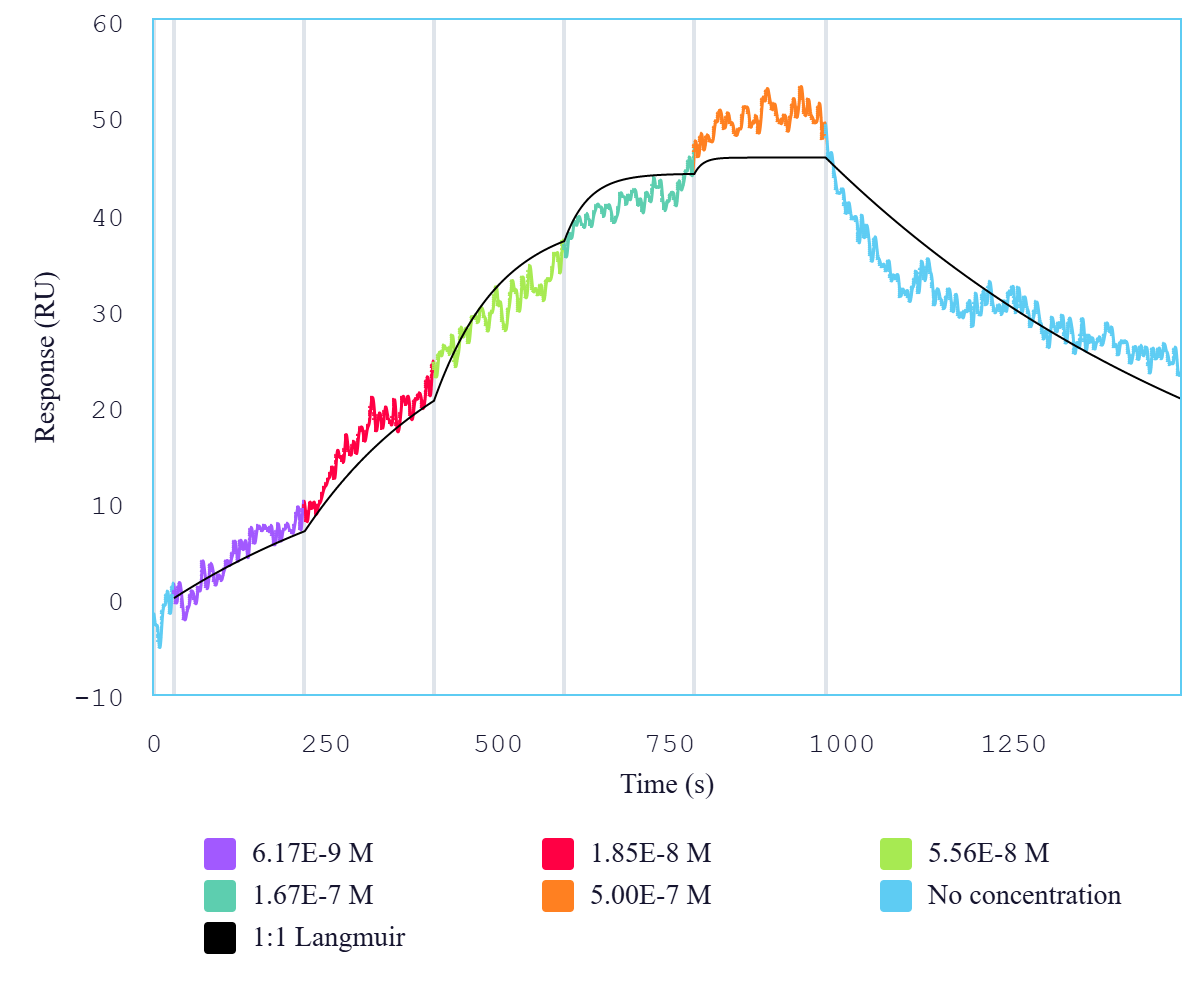 His tag (Cat. No. CSP-25294-01) can bind anti-human FGFR2 polyclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 2.8-11.2 ng/mL (QC tested).
His tag (Cat. No. CSP-25294-01) can bind anti-human FGFR2 polyclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 2.8-11.2 ng/mL (QC tested).