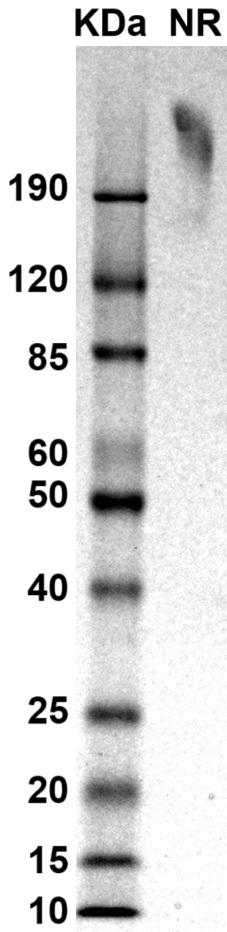
 MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: VEGFR2 dimer under non-reduced condition
MW: Molecular Weight marker reduced condition
NR: VEGFR2 dimer under non-reduced condition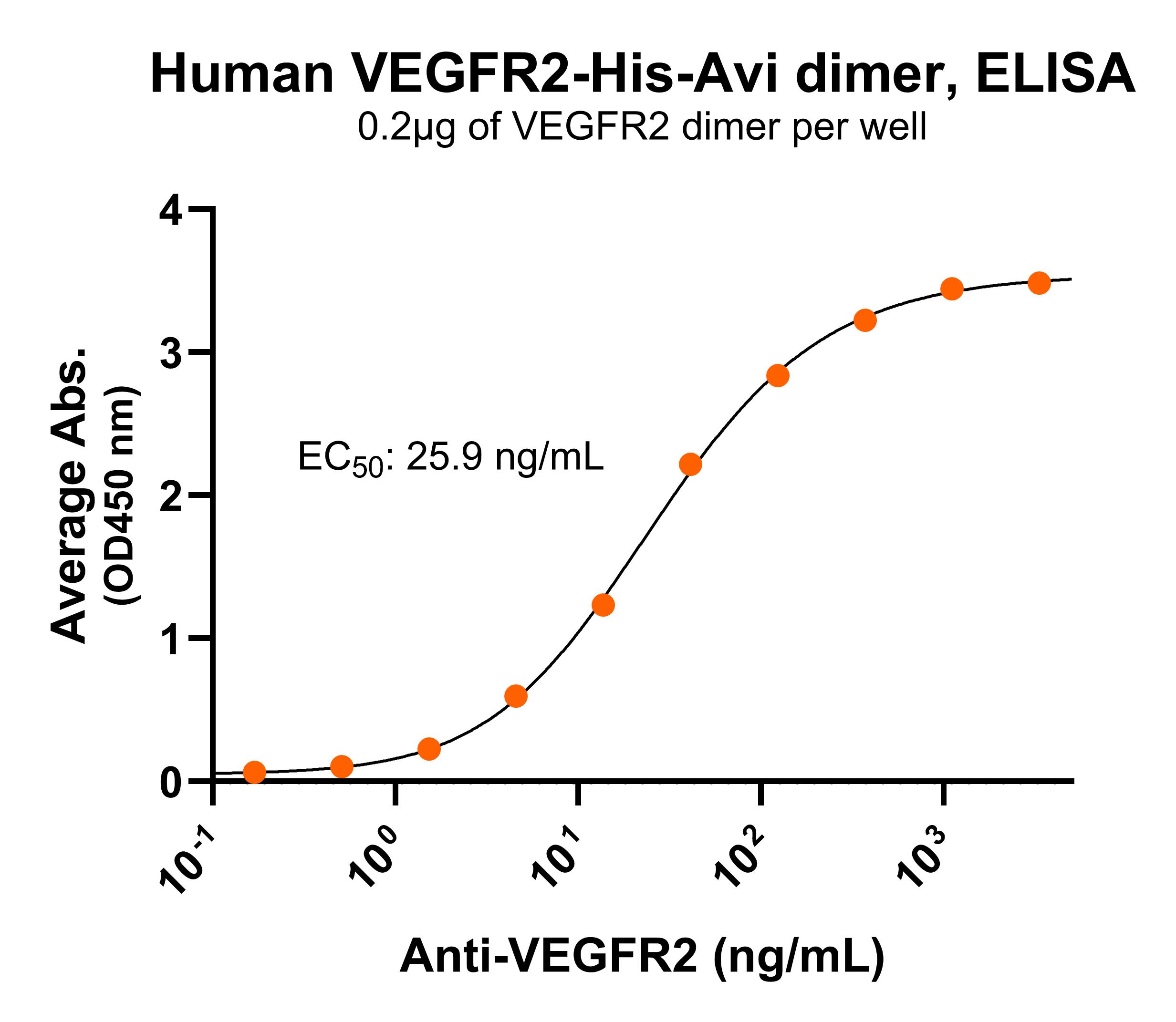 Immobilized human VEGFR2-His-Avi dimer protein (CSP-25127-03) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 13-51.8 ng/mL (QC tested).
Immobilized human VEGFR2-His-Avi dimer protein (CSP-25127-03) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-human VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody with half maximal effective concentration (EC50) range of 13-51.8 ng/mL (QC tested).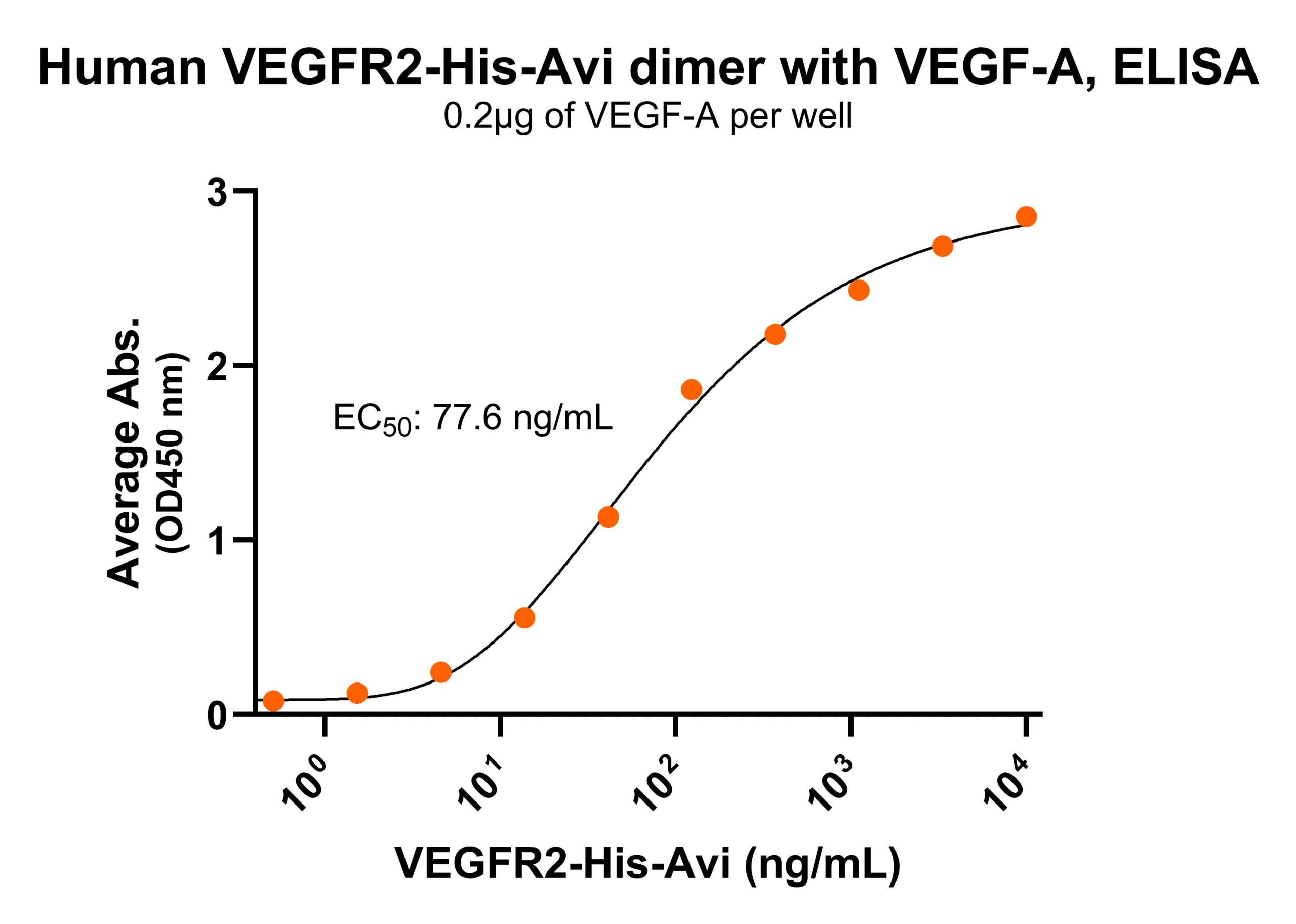 Immobilized human VEGF-A 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind human VEGFR2 dimer protein
Immobilized human VEGF-A 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind human VEGFR2 dimer proteinFor Research Use Only (RUO)