Bioactive, Recombinant Human GLUT1 Full-Length Protein, Displayed on Nanoparticles
| Product Code | CMP-24021 |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
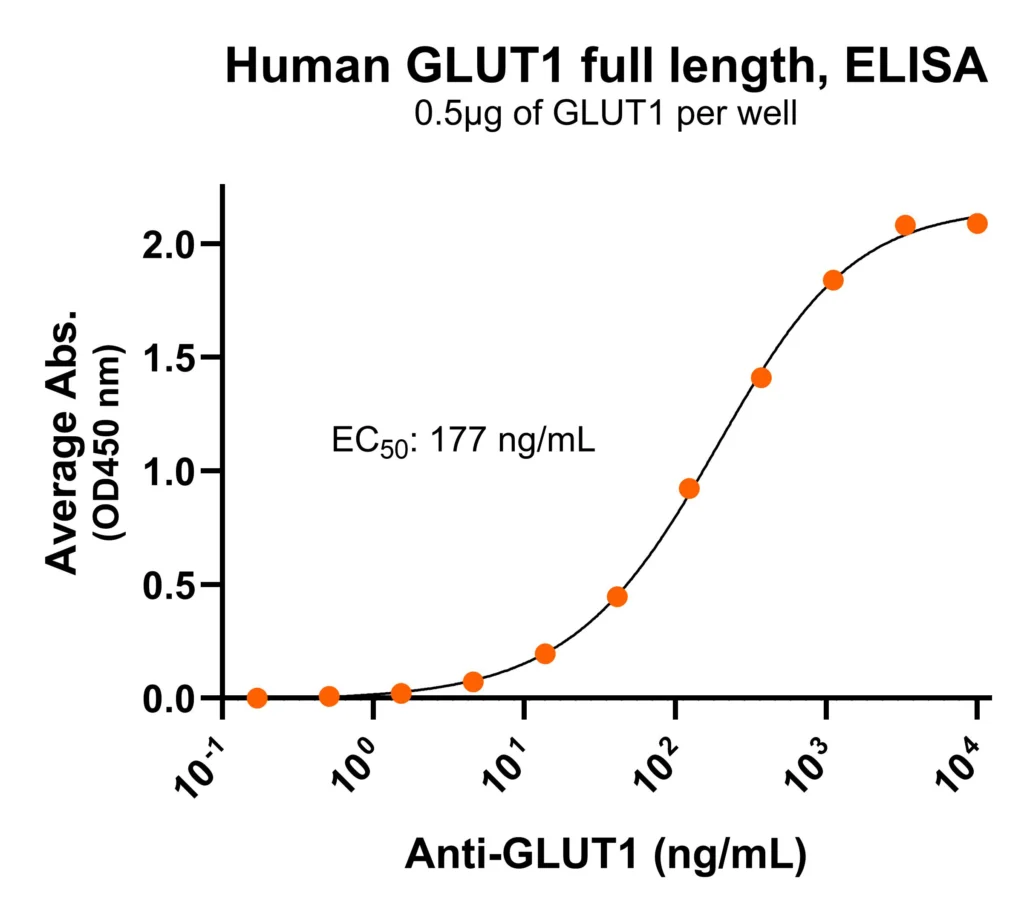
| Verified Applications | ELISA for GLUT1-specific antibody binding assays. |
| Amino Acid Range | M1-V492 |
For Research Use Only
Price: $550.00
Price: $900.00
Price: $1,150.00
Price: $2,200.00
Price: $7,040.00
Specifications
Formulation: 0.2μm filtered PBS, pH 7.4
Shipping: Frozen Dry Ice
Storage: -80°C
Protein Name: GLUT1
UniProt #: P11166
Protein Construct: The human GLUT1 full-length protein is displayed on nanoparticles and mimics the native protein conformation on the cell surface.
Background
Human Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) is a 12-transmembrane protein that facilitates glucose transport. GLUT1 is also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1). GLUT1 is a ubiquitously expressed glucose transporter responsible for basal glucose uptake. It plays a central role in cellular metabolism and is upregulated in response to hypoxia and metabolic stress to meet energetic and biosynthetic demands. GLUT1 mediates glucose transport by undergoing conformational shifts across the plasma membrane, allowing facilitated diffusion of glucose into cells. The GLUT1 crystal structure confirms a 12-transmembrane topology with both the N- and C- termini located intracellularly. GLUT1 is highly expressed in erythrocytes (red blood cells) and the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and present in placenta, kidneys, and endothelium of the central nerve system. GLUT1 is also a receptor used by human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV) to gain entry into target cells. GLUT1 is clinically significant due to its role in glucose transport, especially across the blood-brain barrier. GLUT1 gene mutation can result in several diseases. GLUT1 overexpression is also a hallmark of many cancers. Elevated GLUT1 enhances tumor glucose uptake, acidifies the tumor microenvironment, and contributes to immune evasion by outcompeting infiltrating T cells for glucose and impairing effector function. This makes GLUT1 a potential dual-action target—modulating tumor metabolism and immune response simultaneously.
Alternate Names: solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), DYT18, DYT9, EIG12, GLUT, GLUT-1, GLUT1DS, HTLVR, SDCHCN